Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums. The gums around the teeth become red swollen and tender and bleed when brushing.
If gingivitis is not treated then it can turn into periodontal disease. There are a number of types of periodontal disease and they all affect the tissues supporting the teeth. As this disease progresses the supporting bone around the teeth is lost, and the teeth become loose. This will lead to teeth eventually falling out. This is the most common form of people loosing teeth. The disease develops very slowly in most people, and it can be slowed down to a rate that should allow you to keep most of your teeth for life.
Many of the bacteria in plaque are completely harmless, but there are some that have been shown to be the main cause of gum disease. Plaque will harden into something called calculus another name for it is ‘tartar’. As calculus forms around the gums, the plaque underneath releases poisons causing the gums to become irritated and inflamed. The gums begin to pull away from the teeth and the gaps become infected. If gum disease is not treated promptly, the bone supporting the teeth is destroyed and healthy teeth can become loose and fall out.
To prevent and treat gum disease, you need to make sure you remove all the plaque from your teeth every day. This is done by brushing and flossing and use of other dental aids
Smokers are more prone to gum disease. The gums are affected because smoking causes a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream, so the infected gums fail to heal.
Gum disease can progress painlessly on the whole so that you do notice the damage it is doing. However, the bacteria are sometimes more active and this makes your gums sore. This can lead to gum abscesses. The bone supporting the teeth can be lost. The treatment of gum disease becomes more difficult.
First signs of gum disease is blood on the toothbrush after cleaning your teeth. leaving a bad taste in your mouth. Your breath may smell unpleasant.
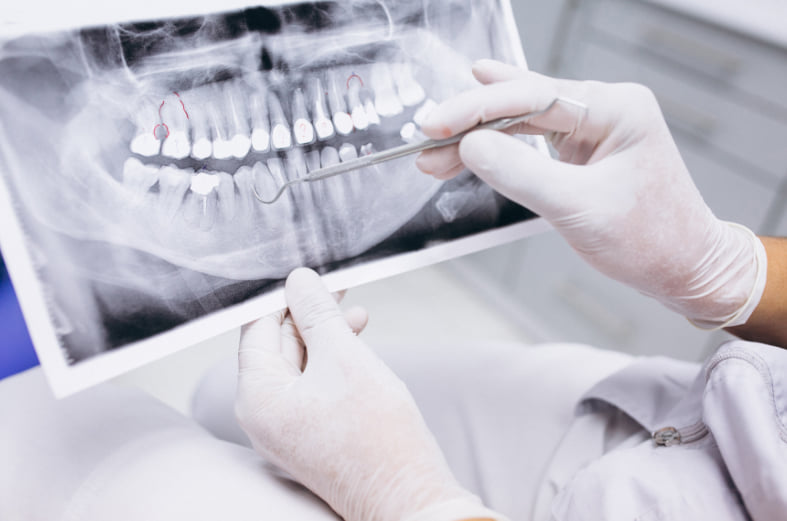
Visit one of our team for a thorough dental health check of your teeth and gums. They will take measurements around the gum and pockets around each tooth to see if there is any sign that periodontal disease has started. X-rays may also be needed to see the amount of bone that has been lost. This assessment is very important, so the correct treatment can be started.
Your teeth and gums need to be cleaned thoroughly to remove the plaque (de-scaling, root planing). You will be advised on shown use of correct dental aids to remove plaque successfully yourself (e.g. electric toothbrush, inter-dental brushes, flossing,mouthrinses), cleaning all surfaces of your teeth thoroughly and effectively. This may take a number of visits with the dentist or hygienist. Once your teeth are clean, it maybe necessary further cleaning of the roots of the teeth, to make sure that the pockets of bacteria are removed.
The periodontal diseases can be controlled, you must make sure you remove plaque every day, and go for regular visits.
©2025 West Road Dental Practice | Created by RAK DESIGN